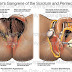
1- Gross specimen of Renal infarction:
The kidney is cut in half along its longitudinal axis, exposing :
(A.) the cortex
(B.) the medulla
(C.) a minor calyx .
The pyramidal shaped infarct is pale as compared to the adjacent normal cortex. Why? as the wedge shape of this zone of coagulative necrosis resulting from loss of blood supply with resultant tissue ischemia that produces the pale infarct.
The arrow points to a line of hyperemia that represents the interface between normal and necrotic tissue.
2- Microscopic section of Renal infarction:
* The thick arrow points to glomerulus in an area of coagulation (ischemic) necrosis.
* The thin arrow points to a glomerulus which is in the interface between necrotic and normal kidney.

Custom Search
Popular Posts
-
W ind --- pneumonia, atelectasis at 1st 24- 48 hours W ater --- urinary tract infection at Anytime after post op day 3 W ound --- wound ...
-
Raccoon Eyes. Ecchymosis in the periorbital area, resulting from bleeding from a fracture site in the anterior portion of the skull base. Th...
-
Lymph Nodes : The major lymph node groups are located along the anterior and posterior aspects of the neck and on the underside of the jaw. ...
-
Fournier's gangrene is a rare condition and delayed treatment results in fatal outcome. We managed a case of Fournier's gangrene by...
-
Viewed posteriorly the right kidney has its upper edge opposite the 11th dorsal spine and the lower edge of the 11th rib. Its lower edge is ...
-
If you are palpating a swelling like an abdominal swelling infront of the aorta, You have to decide whether the mass you feel is pulsatile/e...
-
This raised skin lesion with a central necrotic area has the appearances of a keratoacanthoma. The natural history of these lesions is that...
-
The sphenoid bone carries its share of creating part of the base of the cranium. While it can be seen laterally and inferiorly, the shape of...