Custom Search
Showing posts with label GYNACOLOGY AND OBESTATRIC. Show all posts
Showing posts with label GYNACOLOGY AND OBESTATRIC. Show all posts
Menstrual Cycle explanation
This animation video explains the biological processes of Menstruation and the physiology of Menstrual Cycle
Botox injections into the bladder
A short video demonstration injections of diluted Botulinum toxin "Botox"into the bladder.
The operation takes approximately 10 minutes and is done as a day-case procedure. It is usually well tolerated under local anaesthesia, but for some women a general anaesthetic may be the preferred option. A very fine needle is inserted into the bladder through a cystoscope , and the diluted Botulinum toxin is then injected into 15-20 sites in the bladder wall.
This treatment is suitable for women with severe urgency, frequency, and urge-incontinence that is unresponsive to other treatment, such as bladder retraining and medications.
The operation takes approximately 10 minutes and is done as a day-case procedure. It is usually well tolerated under local anaesthesia, but for some women a general anaesthetic may be the preferred option. A very fine needle is inserted into the bladder through a cystoscope , and the diluted Botulinum toxin is then injected into 15-20 sites in the bladder wall.
This treatment is suitable for women with severe urgency, frequency, and urge-incontinence that is unresponsive to other treatment, such as bladder retraining and medications.
ALCOHOL as Teratogen :Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
In many countries alcohol is the Most common teratogen.And the severity of spectrum of effects in the neonate correlates with the amount of alcohol consumed , ranging from mild reduction in cerebral function to classic fetal alcohol syndrome .
* Palpebral fissure - short opening of eye
* Epicanthal folds - fold of skin at inside of corner of eye
* Midface - flat
* Nasal Bridge - low
* Philtrum - Indistinct, vertical grooves between nose and mouth
* Upper Lip - thin
* Micrognathia - small jaw
* Ears - curve at top part of outer ear is underdeveloped and folded over parallel to curve beneath. Gives the appearance of a "railroad track"
It also associated with :
#Mild to severe mental retardation resulting in learning difficulties.
#Low birth weight and height that persists through early childhood.
#Abnormalities of the heart and other organs.
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome. Notice the depressed nasal bridge, flat philtrum, long upper lip, and thin vermillion border.
Facial features of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS)
* Microcephaly - leads to small head circumference* Palpebral fissure - short opening of eye
* Epicanthal folds - fold of skin at inside of corner of eye
* Midface - flat
* Nasal Bridge - low
* Philtrum - Indistinct, vertical grooves between nose and mouth
* Upper Lip - thin
* Micrognathia - small jaw
* Ears - curve at top part of outer ear is underdeveloped and folded over parallel to curve beneath. Gives the appearance of a "railroad track"
It also associated with :
#Mild to severe mental retardation resulting in learning difficulties.
#Low birth weight and height that persists through early childhood.
#Abnormalities of the heart and other organs.
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome. Notice the depressed nasal bridge, flat philtrum, long upper lip, and thin vermillion border.
Magnesium sulfate as the drug of choice for controlling eclamptic seizures
The drug of choice for controlling eclamptic seizures is
- A) hydralazine
- B) phenobarbital
- C) phenytoin
- D) diazepam
- E) magnesium sulfate
Answer and Discussion
The answer is E.
In the United States, magnesium sulfate is considered the drug of choice for controlling eclamptic seizures. Fewer intubations are required in the neonates of eclamptic women who are treated with magnesium sulfate. In addition, fewer newborns require placement in neonatal intensive care units. In the treatment of eclampsia and preeclampsia, magnesium sulfate is often given according to established protocols. If serum magnesium levels exceed 10 mEq/L (5 mmol/L), respiratory depression can occur. This problem may be counteracted by the rapid intravenous infusion of 10% calcium gluconate. Magnesium sulfate should be used with caution in patients with impaired renal or cardiac status. It should not be used in patients with myasthenia gravis.
iron deficiency anemia in pregnancy
A 22-year-old woman is pregnant and at 14-week gestation. Her hemoglobin level is 9 g/dL. She asks why she could have iron deficiency when she is no longer menstruating. Which of the following is the best explanation?
( B ). Iron deficiency occurs in pregnancy as a result of the expanded blood volume and active transport of iron to the fetus.
- A.Occult gastrointestinal blood loss
- B.Expanded blood volume and transport to the fetus
- C.Hemolysis
- D.Iron losses as a result of relative alkalosis of pregnancy
( B ). Iron deficiency occurs in pregnancy as a result of the expanded blood volume and active transport of iron to the fetus.
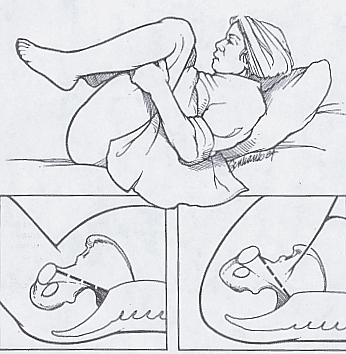
McRoberts Maneuver for Shoulder Dystocia
A 26-year-old woman is having difficulty delivering her 1st child. You suspect shoulder dystocia and ask the mother to stop pushing and notify your staff. The next appropriate step is ?
- A) place the mother in the left lateral position
- B) perform McRoberts' maneuver
- C) apply fundal pressure
- D) the Rubin maneuver (reverse Woods screw)
- E) perform a cesarean section
Answer and Discussion
The answer is B.
The recommended sequence for reducing shoulder dystocia begins with calling for help and asking the mother to stop her pushing efforts. The first step is the McRoberts' maneuver, in which assistants hyperflex the mother's hips against her abdomen, thereby rotating the symphysis pubis anteriorly and decreasing the forces needed to deliver the fetal shoulders.
A recent retrospective study found this maneuver to be the safest and most successful technique for relieving shoulder dystocia. An assistant can add gentle posterolateral suprapubic pressure while the physician continues moderate posterior traction on the fetal head. Fundal pressure should be avoided, because it tends to increase the impaction.
Robotic Surgery
The Center for Reproductive Medicine and Robotic Surgery is a state of the art fertility and robotic surgery center that combines innovative advanced reproductive technology and latest Robotic surgical techniques with a holistic and compassionate approach to patient care.
Minimally Invasive Robotic Surgery for Hysterectomy
Robotic surgery enables physicians to perform minimally invasive surgery that was not possible with simple laparoscopic instruments. Its one of the greatest advancements in surgery during our lifetime. With the robots high definition camera, 10 times magnification and 540 degrees of movement we are able to perform surgery that could not be accomplished with traditional methods.
Carolina Robotic center is a division of WHA Midcarolina obstetrics and Gynecology P.A.
Carolina Robotic center is a division of WHA Midcarolina obstetrics and Gynecology P.A.
Estrogen as an initial treatment for symptomatic labial adhesions
The initial treatment of choice for symptomatic labial adhesions is :
A) testosterone cream
B) estrogen cream
C) GnRH antagonist
D) hydrocortisone cream
E) surgical separation
The answer is: ( B ).
Labial adhesions are common in prepubertal females. The cause is thought related to low levels of circulating estrogen. Most women with small areas of labial adhesions are asymptomatic. However, interference with urination or accumulation of urine behind the adhesion can lead to discomfort and symptoms. Dysuria and recurrent vulvar and vaginal infections are associated symptoms. In rare situations urinary retention may occur. Asymptomatic labial fusion usually does not require treatment. Symptomatic adhesions may be treated with a short course of estrogen cream applied twice daily for 7 to 10 days; this may separate the labia.
A new alternative treatment is to use estrogen transdermal patches in close proximity to the labia. When medical treatment fails or if severe urinary symptoms exist, surgical separation of the labia is indicated. This can be done as an office procedure using 1% to 2% topical xylocaine gel. Because of inadequate levels of estrogen, recurrences of labial adhesion are common until puberty. Following puberty, the condition usually resolves spontaneously. Improved hygiene and removal of vulvar irritants may help prevent recurrences.
A) testosterone cream
B) estrogen cream
C) GnRH antagonist
D) hydrocortisone cream
E) surgical separation
Answer and Discussion
The answer is: ( B ).
Labial adhesions are common in prepubertal females. The cause is thought related to low levels of circulating estrogen. Most women with small areas of labial adhesions are asymptomatic. However, interference with urination or accumulation of urine behind the adhesion can lead to discomfort and symptoms. Dysuria and recurrent vulvar and vaginal infections are associated symptoms. In rare situations urinary retention may occur. Asymptomatic labial fusion usually does not require treatment. Symptomatic adhesions may be treated with a short course of estrogen cream applied twice daily for 7 to 10 days; this may separate the labia.
A new alternative treatment is to use estrogen transdermal patches in close proximity to the labia. When medical treatment fails or if severe urinary symptoms exist, surgical separation of the labia is indicated. This can be done as an office procedure using 1% to 2% topical xylocaine gel. Because of inadequate levels of estrogen, recurrences of labial adhesion are common until puberty. Following puberty, the condition usually resolves spontaneously. Improved hygiene and removal of vulvar irritants may help prevent recurrences.
vaccinations during pregnancy
A 30 year old pregnant lady in her 20th week of gestation. She is asking you about routine vaccinations during pregnancy and you told her that routine immunizations during pregnancy is best avoided because of theoretical risks to the fetus, however many vaccines are safe and can be given during pregnancy period and in special conditions . Which one of the following vaccines is contraindicated in this lady :
a) Tetanus toxoid.
b) Influenza vaccine.
c) Pneumococcal vaccine.
d) Rubella.
e) Diphtheria toxoid.
The correct answer is D
Explanation
Because of the theoretical risks to the fetus and real litigation to the practitioner, routine immunization of pregnant women is best avoided. However, wherever hygienic conditions during delivery can not be guaranteed, it is essential to ensure that pregnant women are immune to tetanus: the transfer of maternal anti-toxin is an important means of preventing neonatal tetanus, and pregnant women can safely receive tetanus as well as diphtheria toxoids.
Although live-virus vaccines in general should withheld during pregnancy, polio and yellow fever vaccines are exceptions and may be administered if the risk of exposure to disease is great. If indicated, some inactivated vaccines (HBV, influenza and pneumococcal vaccines) are safe for pregnant women. Known pregnancy is considered a contraindication to the receipt of rubella, measles, mumps and varicella vaccines. Although of theoretical concern, no cases of congenital rubella syndrome or abnormalities attributable to rubella vaccine virus have been observed in infants born to susceptible mothers who received rubella vaccine during pregnancy.
a) Tetanus toxoid.
b) Influenza vaccine.
c) Pneumococcal vaccine.
d) Rubella.
e) Diphtheria toxoid.
The correct answer is D
Explanation
Because of the theoretical risks to the fetus and real litigation to the practitioner, routine immunization of pregnant women is best avoided. However, wherever hygienic conditions during delivery can not be guaranteed, it is essential to ensure that pregnant women are immune to tetanus: the transfer of maternal anti-toxin is an important means of preventing neonatal tetanus, and pregnant women can safely receive tetanus as well as diphtheria toxoids.
Although live-virus vaccines in general should withheld during pregnancy, polio and yellow fever vaccines are exceptions and may be administered if the risk of exposure to disease is great. If indicated, some inactivated vaccines (HBV, influenza and pneumococcal vaccines) are safe for pregnant women. Known pregnancy is considered a contraindication to the receipt of rubella, measles, mumps and varicella vaccines. Although of theoretical concern, no cases of congenital rubella syndrome or abnormalities attributable to rubella vaccine virus have been observed in infants born to susceptible mothers who received rubella vaccine during pregnancy.
Some contraindication to Exercise during pregnancy
Which of the following is not a contraindication to exercise during pregnancy?
Although supportive data is limited, there appears to be no reason why women who are in good health should not be permitted to engage in exercise while pregnant. However, women with medical or obstetric complications should be encouraged to avoid vigorous physical activity. Given the current lack of data, a conservative approach is warranted when doubt exists.
Contraindications to exercise during pregnancy include PIH, preterm rupture of membranes, preterm labor during the prior or current pregnancy, incompetent cervix or cerclage placement, persistent second- or third-trimester bleeding, placenta previa, and intrauterine growth retardation.
- A) Pregnancy induced hypertension (PIH)
- B) Incompetent cervix
- C) Preterm labor during a prior pregnancy
- D) Placenta previa
- E) All are contraindications
Although supportive data is limited, there appears to be no reason why women who are in good health should not be permitted to engage in exercise while pregnant. However, women with medical or obstetric complications should be encouraged to avoid vigorous physical activity. Given the current lack of data, a conservative approach is warranted when doubt exists.
Contraindications to exercise during pregnancy include PIH, preterm rupture of membranes, preterm labor during the prior or current pregnancy, incompetent cervix or cerclage placement, persistent second- or third-trimester bleeding, placenta previa, and intrauterine growth retardation.
Presentation of Atrophic vaginitis
A 64 y old woman presents with vaginal bleeding similar to “spotting” that has occurred daily for 1 mo. Her last menses was at age 50 and she has been healthy her entire life. She denies fever,weight loss, or abdominal pain.Physical examination is normal.
the most likely diagnosis is?
The answer is ( a ).
The most commoncause of postmenopausal vaginal bleeding is atrophic vaginitis (with or without trauma).
Endometriosis is the most common cause of infertility;patients present with dyspareunia (painful intercourse), abnormal vaginal bleeding, and pelvic pain. Uterine leiomyomas (uterine fibroids) change in size with the menstrual cycle but regress in size during menopause. Often the fibroid is palpable on pelvic examination. Polycystic ovarian syndrome (Stein-Leventhal syndrome) affects younger women (15–30). The etiology of polycystic ovary syndrome is unknown; patients present with amenorrhea, obesity, hirsutism, and infertility. All postmenopausal women with vaginal bleeding require a biopsy to rule out endometrial carcinoma.
the most likely diagnosis is?
- a.Atrophic vaginitis
- b.Endometriosis
- c.Uterine leiomyoma
- d.Endometrial carcinoma
- e.Polycystic ovarian syndrome
The answer is ( a ).
The most commoncause of postmenopausal vaginal bleeding is atrophic vaginitis (with or without trauma).
Endometriosis is the most common cause of infertility;patients present with dyspareunia (painful intercourse), abnormal vaginal bleeding, and pelvic pain. Uterine leiomyomas (uterine fibroids) change in size with the menstrual cycle but regress in size during menopause. Often the fibroid is palpable on pelvic examination. Polycystic ovarian syndrome (Stein-Leventhal syndrome) affects younger women (15–30). The etiology of polycystic ovary syndrome is unknown; patients present with amenorrhea, obesity, hirsutism, and infertility. All postmenopausal women with vaginal bleeding require a biopsy to rule out endometrial carcinoma.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
Popular Posts
-
W ind --- pneumonia, atelectasis at 1st 24- 48 hours W ater --- urinary tract infection at Anytime after post op day 3 W ound --- wound ...
-
Raccoon Eyes. Ecchymosis in the periorbital area, resulting from bleeding from a fracture site in the anterior portion of the skull base. Th...
-
Lymph Nodes : The major lymph node groups are located along the anterior and posterior aspects of the neck and on the underside of the jaw. ...
-
Fournier's gangrene is a rare condition and delayed treatment results in fatal outcome. We managed a case of Fournier's gangrene by...
-
Viewed posteriorly the right kidney has its upper edge opposite the 11th dorsal spine and the lower edge of the 11th rib. Its lower edge is ...
-
If you are palpating a swelling like an abdominal swelling infront of the aorta, You have to decide whether the mass you feel is pulsatile/e...
-
This raised skin lesion with a central necrotic area has the appearances of a keratoacanthoma. The natural history of these lesions is that...
-
The sphenoid bone carries its share of creating part of the base of the cranium. While it can be seen laterally and inferiorly, the shape of...