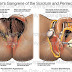
The endolymphatic shunt operation consists of opening the mastoid bone and identifying the endolymphatic sac which is located in the posterior fossa dura.
To find the sac, the sigmoid sinus is denuded of its bony cover except for a small rectangle of thin bone named Bill's Island, after Dr. William House. The sigmoid sinus is then collapsed with gentle pressure and the sac exposed behind the posterior semicircular canal.
The sac is then incised and a shunt tube is inserted. The picture shows a Huang-Gibson tube with a one-way valve that allows fluid to seep out but not back into the sac. This procedure decreases the endolymphatic fluid pressure