Actinic Keratosis Actinic keratosis (AK), or solar keratosis, or senile keratosis is a precancerous skin condition that develops in the skin when exposed to sun, hydrocarbons, and arsenicals and is more common in light-skinned people When the human skin is exposed to the sun, the UV-B rays from the sun damage the dermis and epidermis. The epidermis is thinned and damaged cells calls fibroblasts cause synthesis of abnormal dermal elastic fibers within the superficial dermis that give the characteristic appearance of actinic keratosis. Actinic keratoses are small, noticeable, red-brown patches that don't fade away and have a characteristic rough texture accompanied by itching and burning. The lesions are generally 1-3mm in size, occur in clusters, and generally occur in sun exposed areas like the face, neck, and hands.Actinic keratosis has physical characteristics that allow dermatologists to visually identify them. If there is any indication of the possibility of cancer, a skin biopsy is recommended.There are several options to treat AK, the decision on treatment methodology is based on the nature of the lesion, age and health.Actinin keratosis can be treated by:CryosurgeryCurettage and Electro dissectionSurgical ExcisionDermabrasionTopical medicationsActinic keratosis can be prevented by avoiding prolonged exposure to the sun, wearing protective clothing, using sunscreen lotion and sun glasses and regular skin self-examination.

Custom Search
Actinic keratosis Animation
Actinic Keratosis Actinic keratosis (AK), or solar keratosis, or senile keratosis is a precancerous skin condition that develops in the skin when exposed to sun, hydrocarbons, and arsenicals and is more common in light-skinned people When the human skin is exposed to the sun, the UV-B rays from the sun damage the dermis and epidermis. The epidermis is thinned and damaged cells calls fibroblasts cause synthesis of abnormal dermal elastic fibers within the superficial dermis that give the characteristic appearance of actinic keratosis. Actinic keratoses are small, noticeable, red-brown patches that don't fade away and have a characteristic rough texture accompanied by itching and burning. The lesions are generally 1-3mm in size, occur in clusters, and generally occur in sun exposed areas like the face, neck, and hands.Actinic keratosis has physical characteristics that allow dermatologists to visually identify them. If there is any indication of the possibility of cancer, a skin biopsy is recommended.There are several options to treat AK, the decision on treatment methodology is based on the nature of the lesion, age and health.Actinin keratosis can be treated by:CryosurgeryCurettage and Electro dissectionSurgical ExcisionDermabrasionTopical medicationsActinic keratosis can be prevented by avoiding prolonged exposure to the sun, wearing protective clothing, using sunscreen lotion and sun glasses and regular skin self-examination.
Popular Posts
-
W ind --- pneumonia, atelectasis at 1st 24- 48 hours W ater --- urinary tract infection at Anytime after post op day 3 W ound --- wound ...
-
Raccoon Eyes. Ecchymosis in the periorbital area, resulting from bleeding from a fracture site in the anterior portion of the skull base. Th...
-
Lymph Nodes : The major lymph node groups are located along the anterior and posterior aspects of the neck and on the underside of the jaw. ...
-
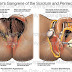
Fournier's gangrene is a rare condition and delayed treatment results in fatal outcome. We managed a case of Fournier's gangrene by...
-
Viewed posteriorly the right kidney has its upper edge opposite the 11th dorsal spine and the lower edge of the 11th rib. Its lower edge is ...
-
If you are palpating a swelling like an abdominal swelling infront of the aorta, You have to decide whether the mass you feel is pulsatile/e...
-
This raised skin lesion with a central necrotic area has the appearances of a keratoacanthoma. The natural history of these lesions is that...
-
The sphenoid bone carries its share of creating part of the base of the cranium. While it can be seen laterally and inferiorly, the shape of...