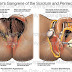
-Pigment stones are often small and occur in patients with either congenital or acquired haemolytic states (5%).
-Cholesterol stones are often large and solitary (15%).
The stones shown are mixed stones and account for approximately 80% of all gallstones.
"Mixed stones are probably a variant of cholesterol stones"
Pathophysiology:
Cholesterol stones result from a change in solubility of bile constituents- Bile acids act as a detergent keeping cholesterol in solution
- Bile acids, lecithin and cholesterol result in the formation of micelles
- Bile is often supersaturated with cholesterol
- This favours the formation of cholesterol microcrystals
- Biliary infection, stasis and changes in gallbladder function can precipitate stone formation
Only 10% of gallstones are symptomatic.Also about 10% of gallstones are radio-opaque and visible on a plain abdominal film.