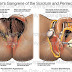
It is a form of drain which Can be inserted transurethrally or suprapubically
*Commonly used to:
1- Alleviate or prevent urinary retention
2- Monitor urine output
* Catheters vary by:
o The material from which they are made (latex, plastic, silastic, teflon-coated)
o The length of the catheter (38 cm 'male' or '22 cm 'female')
o The diameter of the catheter (10 Fr to 24 Fr)
o The number of channels (two or three)
o The size of the balloon ( 5ml to 30 ml)
o The shape of the tip
* Special catheters exist such as:
- Gibbon catheters
- Nelaton catheters
- Tiemann catheters
- Malecot catheters
Complications :
* Paraphimosis
* Blockage
* By-passing
* Infection
* Failure of balloon to deflate
* Urethral strictures
Do's and don'ts of urinary catheters

* Choose an appropriate sized catheter
* Insert using an aseptic technique
* Never insert using force
* Do not inflate the balloon until urine has been seen coming from the catheter
* Record the residual volume
* Do not use a catheter introducer unless you have been trained in its use
* If difficulty is encountered inserting a urinary catheter consider a suprapubic
* Remove at the earliest possibility