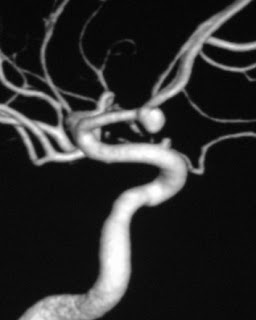
This photo on the right is Photo of a Norwegian blueberry.
Pathology
The aneurysmal pouch is composed of thickened hyalinised intima with the muscular wall & internal elastic lamina being absent.
Comments required on a radiology report:
* size : ideally 3 axis maximum size meansurements
* neck : maximal width of the neck of the aneurysm
* shape and lobulations
* orientation : the direction in which the aneurysm points is often important in both endovascular and surgical planning
This small berry aneurysm projecting inferiorly from the ACOM had pushed into the optic chiasm causing a bitemporal hemianopia, similar to that seen in pituitary lesions.
SAH angiogram